By Prof. Dr Lieven Annemans, expert trainer of the courses
Health Economics for Non-Health-Economists, Basics of Health Economics, and Critical New HTA Developments in Europe: Challenges & Solutions
QALY stands for Quality Adjusted Life Year. The QALY is commonly used in health economic evaluations as a means of quantifying the health effect of a medical intervention or a prevention program and ultimately to help payers allocate healthcare resources.
The Calculation
The QALY can be calculated using the following formula which assumes a utility value (quality of life) between 1 = perfect health and 0 = dead:
Years of Life x Utility Value = #QALYs
This means:
- If a person lives in perfect health for one year, that person will have 1 QALY.
(1 Year of Life × 1 Utility Value = 1 QALY)
- If a person lives in perfect health but only for half a year, that person will have 0.5 QALYs.
(0.5 Years of Life x 1 Utility Value = 0.5 QALYs)
- Conversely, if a person lives for 1 year in a situation with 0.5 utility (half of perfect health), that person will also have 0.5 QALYs.
(1 Year of Life x 0.5 Utility Value = 0.5 QALYs)
In cost-effectiveness studies (or: health economic evaluations) the QALY is used to quantify the effectiveness of, for instance, a new medicine versus the current one. In other words, the current standard of care is taken as the baseline, and the QALYs gained from the new (improved) intervention are counted in addition.
Example
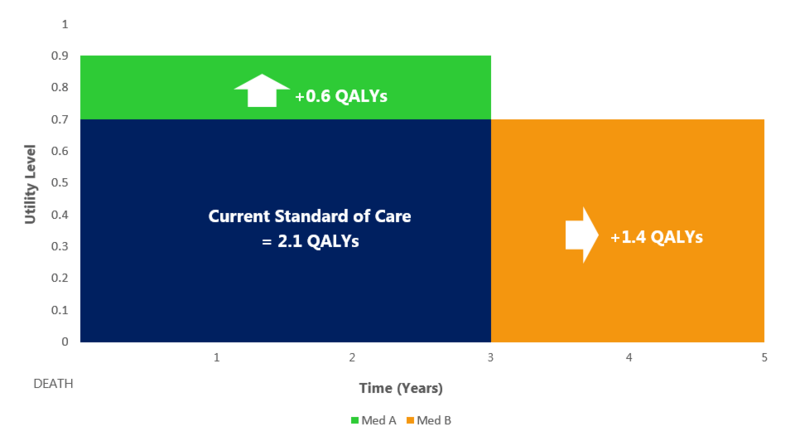
- If a person lives for 3 years with a disease and the current standard of care for that disease means he/she lives with a utility level of 0.7, that person will have 2.1 QALYs.
(3 Years of Life x 0.7 Utility Value = 2.1 QALYs)
- If that person takes a new medicine (Med A) whereby his/her utility level increases to 0.9, that person will now have 2.7 QALYS. Therefore, the benefit of the new medicine will be counted as 0.6 QALYs as this is the increase over the current standard of care.
(3 Years of Life x 0.2 Additional Utility Level = 0.6 QALYs)
- Similarly, if a new medicine (Med B) prolongs the patient’s life by 2 years, at a utility level of 0.7, the new medicine will provide the person with 1.4 additional QALYs.
(2 Years of Additional Life x 0.7 Utility Value = 1.4 QALYs)
In order to be able to compare QALY gains across diseases and therapeutic areas, a comparative scale has been developed to determine the quality of life (utility level) an individual has with a particular disease.
The beauty of the QALY therefore is that it allows you to compare the health effect of a new cancer therapy with the health effect of a new anti-depressant (or with any other medical intervention).
